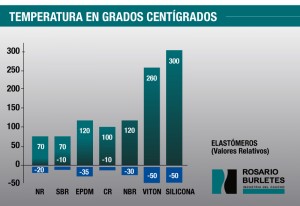
These are the raw materials with which we make our weather strips and molded parts
- SILICONE
Generally used for:
Gaskets for autoclaves - Lighting devices - Food sector
- ACRYLONITRIL
Generally used for:
Gaskets - Diaphragms - Hoses - Tubes and Sleeves - Rollers - NATURAL RUBBER
Generally used for: Tires - Hoses - Coatings - Bushings - Washers - Seals - EPDM
Generally used for:
Gaskets - Radiator hoses - Cable insulation - Aluminum profiles - POLYCOLOROPRENE
Generally used for: Conveyor belts - Cable coatings - Expansion joints - VITON
Generally used for:
Gaskets - Seals - Valves - Chemical industry
- SBR
Generally used for:
Tire covers - Footwear sector - Conveyor belts
PROPERTIES
Mechanics
- Does not have resistance to bending
- Low abrasion resistance
- Poor impact resistance
- Excellent tear resistance
Physical
- Service temperature: -50 ° C to 300 ° C
- Excellent resistance to weathering (oxidation, ozone, sunlight)
- Excellent electrical resistance
- Its permeability to gases is very large
- Arden con dificultad
Chemicals
![]()
- Excellent resistance to water and very poor to water vapor
- Does not have resistance to hydrocarbons (aliphatic, aromatic and chlorinated)
- Good resistance to diluted acids, even concentrates
- Excellent resistance to oils (animal and vegetable)
Applications
PROPERTIES
Mechanics
- Good resistance to bending
- Good resistance to abrasion
- Poor impact resistance
- Good tear resistance
Physical
- Service temperature: -30 ° C to 120 ° C
- Low resistance to weathering (oxidation, ozone, sunlight)
- Does not have electrical resistance
- Low gas permeability
Chemicals

- Good water resistance and moderate to water vapor
- Excellent resistance to aliphatic and moderate hydrocarbons against aromatics and chlorinated
- Good resistance to diluted acids, even concentrates
- Good resistance to oils (animal and vegetable)
- Excellent resistance to gasoline
Applications
PROPERTIES
Mechanics
- Trend to crystallization that reinforces the material causing an excellent mechanical resistance
- Excellent resilience, low hysteresis with little heat generation in the case of repeated deformations
- Excelente resistencia al desgarro, moderada resistencia a la abrasión
- Excellent impact resistance
- Moderate resistance to bending
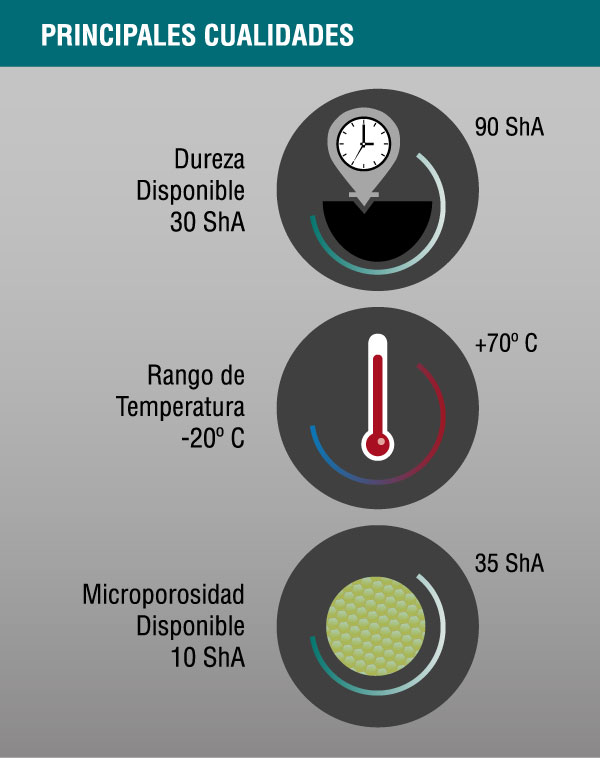
Physical
- Service temperature: -20 ° C to 70 ° C
- Low resistance to weathering (oxidation, ozone, sunlight)
- Moderada resistencia eléctrica
- Very low gas permeability
Chemicals

- Excellent water resistance and good resistance to water vapor
- They do not have resistance to hydrocarbons (aliphatic, aromatic, chlorinated)
- Excellent resistance to diluted acids, moderate in case of higher concentration
- Low resistance to oils (animal and vegetable)
Applications
PROPERTIES
Mechanics
- Moderate resilience
- Moderada resistencia a la abrasión
- Good impact resistance
- Does not have resistance to bending
- Poor resistance to tearing
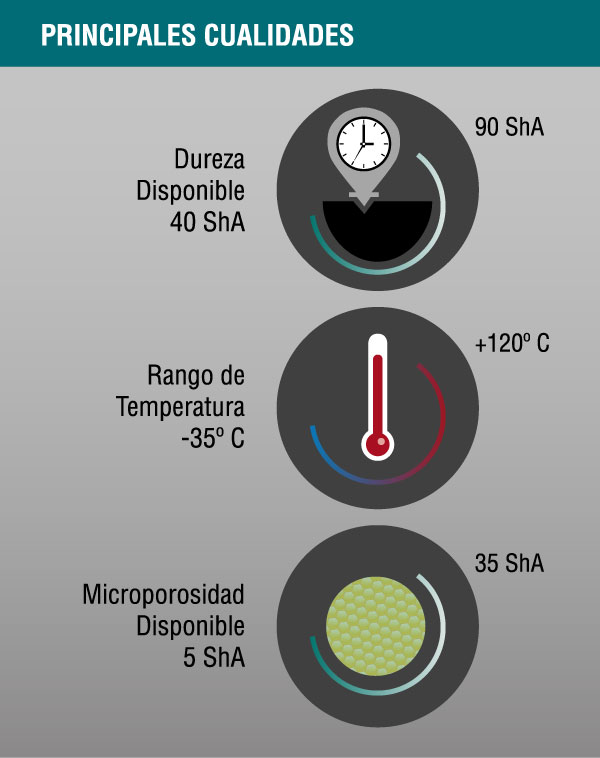
Physical
- Service temperature: -35 ° C to 120 ° C
- Excellent resistance to weathering (oxidation, ozone, sunlight)
- Excellent electrical resistance
- Very low gas permeability
Chemicals
- Excellent resistance to water and water vapor
- They do not have resistance to hydrocarbons (aliphatic, aromatic, chlorinated)
- Excellent resistance to diluted acids, even concentrates
- Good resistance to oils (animal and vegetable)
Applications
PROPERTIES
Mechanics
- Moderate to excellent resistance to bending
- Moderate to excellent abrasion resistance
- Good impact resistance
- Good tear resistance
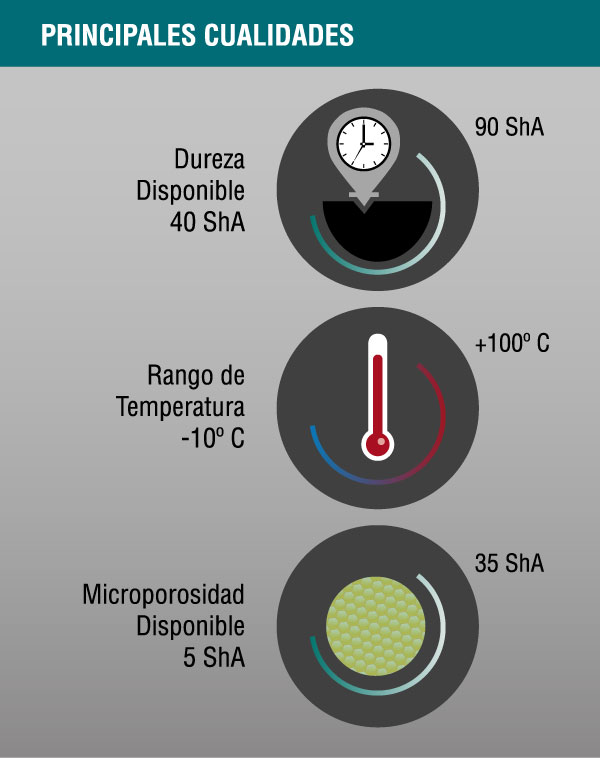
Physical
- Service temperature: -10 ° C to 100 ° C
- Very good resistance to weathering (oxidation, ozone, sunlight)
- Poor electrical resistance
- Low gas permeability
- They burn in the presence of flame but once removed it is self-extinguishing
Chemicals

- Good resistance to water and water vapor
- Good resistance to aromatic hydrocarbons, moderate against aliphatic and null against chlorinated
- Excellent resistance to diluted acids, even concentrates
- Good resistance to oils (animal and vegetable)
Applications
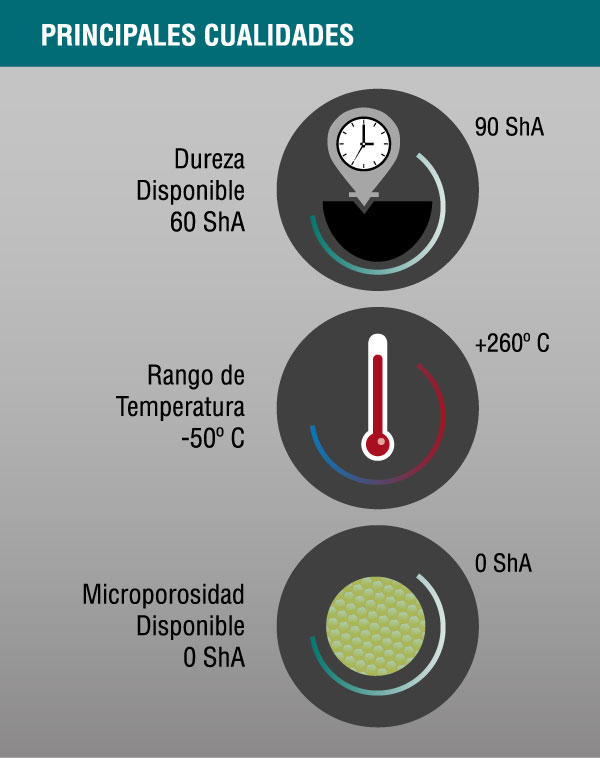
PROPERTIES
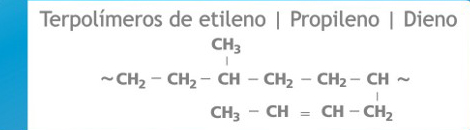
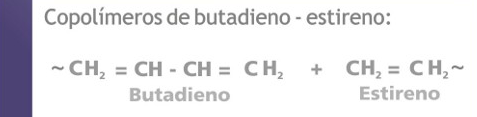
They are copolymers of vinylidene fluoride and hexafluoropropylene:
CH2 = CF2 (vinylidene fluoride) + CF3CF = CF2 (hexafluoropropylene)
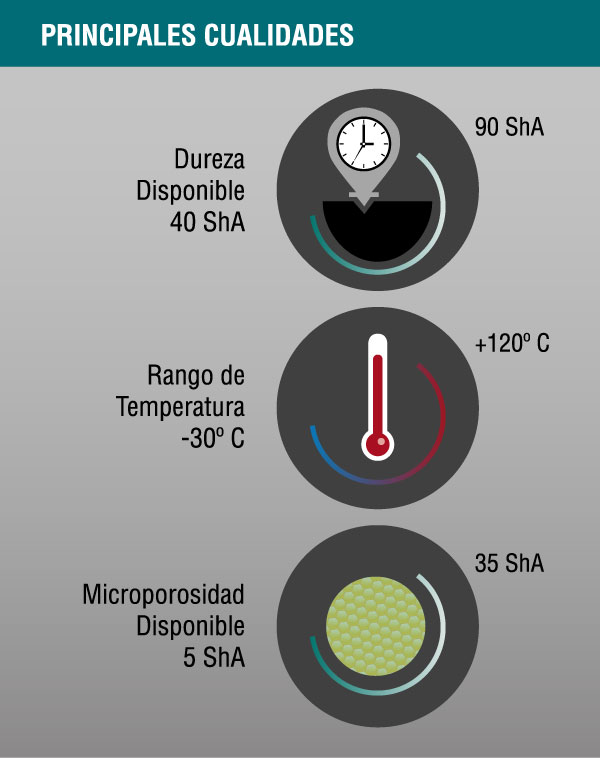
Hardness ranges available:
- Rigid products: 60 ShA - 90 ShA
- Microporous products: not available
Mechanics
- Poor resistance to bending
- Good resistance to abrasion
- Good impact resistance
- Does not have resistance to tearing
Physical
- Service temperature: -50 ° C to 260 ° C
- Excellent resistance to weathering (oxidation, ozone, sunlight)
- Good electrical resistance
- No gas permeability
- They are self-extinguishing
Chemicals

- Excellent water resistance and good water vapor
- Excellent resistance to hydrocarbons (aliphatic, aromatic and chlorinated)
- Excellent resistance to diluted acids, even concentrates
- Excellent resistance to oils (animal and vegetable)
Applications
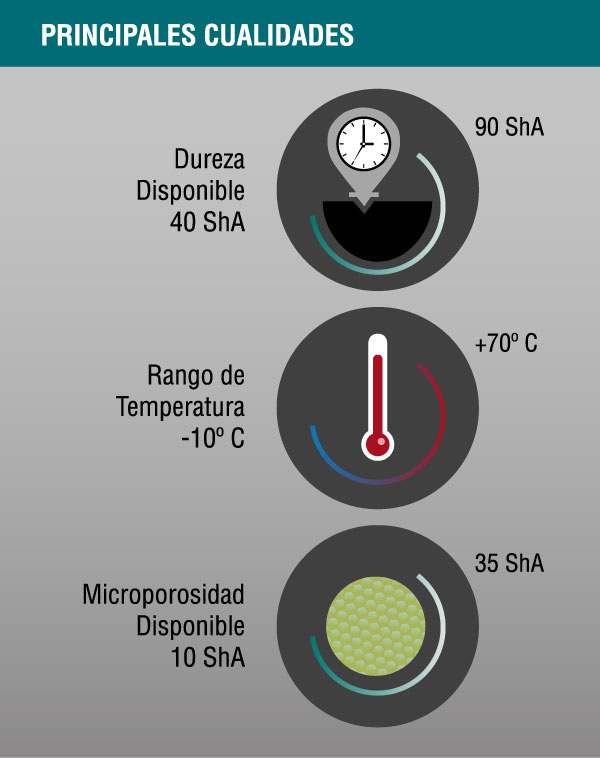
PROPERTIES
Mechanics
- Moderate resilience
- Excellent resistance to abrasion
- Moderate tear resistance
- Excellent impact resistance
- Moderate resistance to bending
Physical
- Service temperature: -10 ° C to 70 ° C
- Low resistance to weathering (oxidation, ozone, sunlight)
- Excellent electrical resistance
- Very low gas permeability
Chemicals
- Good water resistance but poor resistance to water vapor
- They do not have resistance to hydrocarbons (aliphatic, aromatic, chlorinated)
- Low resistance to diluted acids, lower even in case of higher concentration
- Low resistance to oils (animal and vegetable)
Applications
Technical information
Additional information for the application of this product
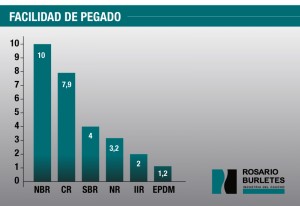
RUBBER / METAL ADHESION
The factor that most influences the ease of adhesion is the type of rubber base and its formulation.
Preparation of the metal:
Cleaning:
Chemistry: Use solvent (eg ethyl, methyl, ketone). Degreaser
Mechanics: Sanding, grinding: Elimination of rust and dry dirt.
Surface Preparation:
Sandblasting: Greater specific adhesion surface.
Final cleaning: Clean again.
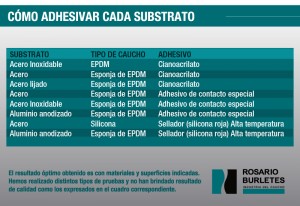
RUBBER / RUBBER ADHESION
Preparation of surfaces
Use solvent to clean surfaces
Let evaporate
If joining ends, cut at 45 °.
Recommended adhesives:
To join rubber / silicone:
Sealers "Siloc", "Orbasil", etc.
To join other rubbers:
Instant hitters: "Loctite", "Ciano", Contact Cement: 3M, etc.
Note: If these procedures are not performed or are not done properly, adhesion may fail. In all cases let dry / cure 24 hours.
ADHESIVE A SUBSTRATE
Steps to follow:
1- Clean the substrate and the type of rubber to be used with liquid that does not deposit fatty residues such as, for example, isopropyl alcohol, trichlorethylene, methyl ethyl ketone, among others.
2- Sand the material and clean it again to remove the impurities.
3- Distribute the adhesive evenly on the 2 surfaces to be glued, in the case of contact adhesive
4- Allow a few minutes to breathe and then proceed to the paste in the case of the contact adhesive.